
It might be useful to create a pivot table and pivot chart at the same time.Alternatively, you can click the Collapse Dialog button and select a table or range of cells in another workbook using the mouse. If you are creating a pivot table from the data in another worksheet or workbook, include the workbook and worksheet names using the following syntax sheet_name!range, for example, Sheet1!$A$1:$E$20.In most cases, it makse sense to place a pivot table in a separate worksheet, this is especially recommended for beginners.In the Location box, click the Collapse Dialog button to choose the first cell where you want to position your table.Ĭlicking OK creates a blank pivot table in the target location, which will look similar to this: Selecting Existing Worksheet will place your table at the specified location in an existing worksheet.Selecting New Worksheet will place a table in a new worksheet starting at cell A1.Then choose the target location for your Excel pivot table:

Make sure the correct table or range of cells is highlighted in the Table/Range field. This will open the Create PivotTable window. Select any cell in the source data table, and then go to the Insert tab > Tables group > PivotTable. To make it easier to maintain your table, you can name your source table by switching to the Design tab and typing the name in the Table Name box the upper right corner of your worksheet.Make sure your source table contains no blank rows or columns, and no subtotals.Add unique, meaningful headings to your columns, they will turn into the field names later.In this context, a dynamic range means that your table will automatically expand and shrink as you add or remove entries, so won't have to worry that your pivot table is missing the latest data.
Using an Excel Table for the source data gives you a very nice benefit - your data range becomes "dynamic". To do this, select all of the data, go to the Insert tab and click Table. Organize your source dataīefore creating a summary report, organize your data into rows and columns, and then convert your data range in to an Excel Table. In fact, you can build your own summary table in just a couple of minutes. But this is not true! Microsoft has been refining the technology for many years, and in the modern versions of Excel, the summary reports are user-friendly are incredibly fast. Many people think that creating a pivot table is burdensome and time-consuming. How to make a pivot table in Excel: quick start And the steps below show how you can quickly create your own pivot table in all versions of Excel. The screenshots above demonstrate just a few of many possible layouts. In just a few mouse clicks, you can get a resilient and easily customizable summary table that totals the numbers by any field you want. However, if you want to compare several facts about each figure, using a pivot table is a far more efficient way. One possible way to sum this long list of numbers by one or several conditions is to use formulas as demonstrated in SUMIF and SUMIFS tutorials.

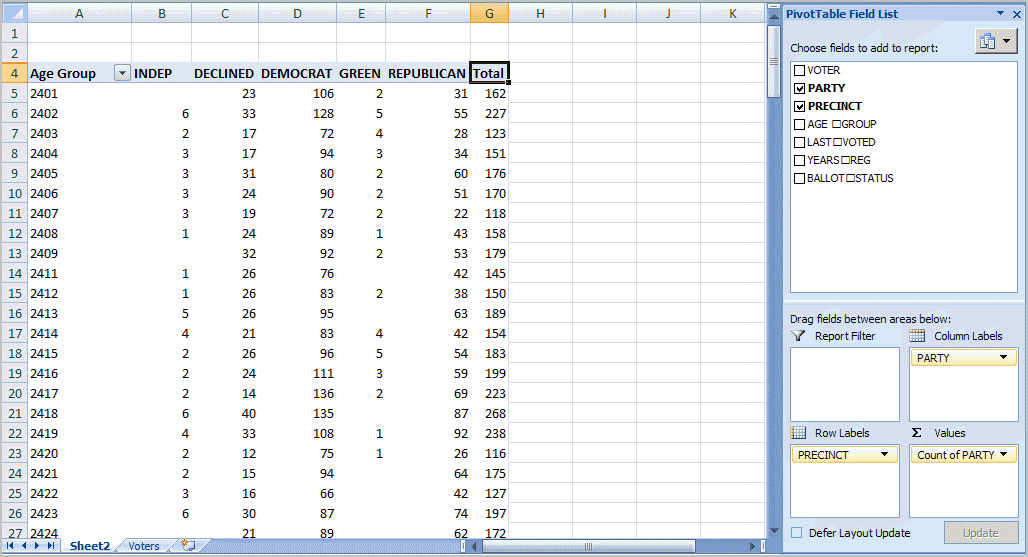
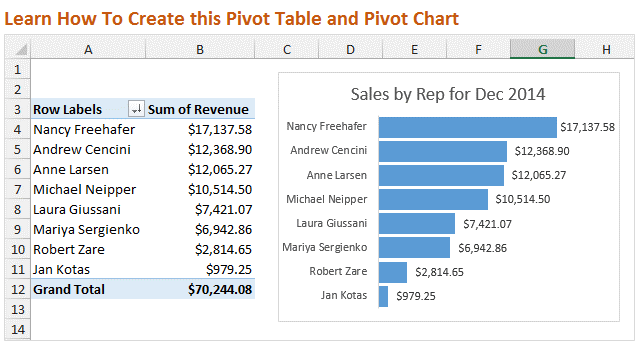
Summarize data by categories and subcategories.Present large amounts of data in a user-friendly way.This rotation or pivoting gave the feature its name.Īn Excel PivotTable is a tool to explore and summarize large amounts of data, analyze related totals and present summary reports designed to: Among other things, it can automatically sort and filter different subsets of data, count totals, calculate average as well as create cross tabulations.Īnother benefit of using pivot tables is that you can set up and change the structure of your summary table simply by dragging and dropping the source table's columns. If you are working with large data sets in Excel, pivot table comes in really handy as a quick way to make an interactive summary from many records. In this tutorial you will learn what a PivotTable is, find a number of examples showing how to create and use pivot tables in all version of Excel 365 through Excel 2007.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
